Coverage analysis
02 Aug 2024To ensure a high standard of code quality, the RTEMS project has set the goal of achieving 100% code coverage in its testing. As part of my contribution to the project, I needed to verify that the code I added was thoroughly tested. This required me to learn how to perform a coverage analysis, which was a new skill I had acquire.
I reached out to one of my mentors, who provided me with a helpful example of how to run a coverage analysis. The example was slightly different from my situation, so i had to adapt it to my necessity. The work i had to do was mainly to change the arhitecture and paths referenced in the commands. Among the files i received there was also a python script, witch also had to be adapted by changhing the referenced architercture at the bottom of the file.
After some different attempts, this is the workflow i ended up with:
- Step 0 : Build the project
Before generating the coverage report it’s necessary to build the project. To be able to generate the coveragereport it’s necessary to enable it, by adding RTEMS_GCOV_COVERAGE = True in the config.ini file.
If the flag is not present, no gcov info will be generated when an excecutable is run.
- Step 1 : Run the Tests
The first step is to run the test, the command i used is this:
rtems-run --rtems-bsp=erc32-sis --log rtems_run.log build/sparc/erc32/testsuites/
In this command --log rtems_run.log specifies that the output of the execution wil be saved in a file named rtems_run.log
- Step 2 : Execute the Python Script
After running the tests, the next step is to process the results using a Python script. I executed the following command:
python run_gcov_tool.py rtems_run.log
This command runs the run_gcov_tool.py script, using the rtems_run.log file generated in the previous step as input. The script processes the log file and prepares the data for coverage analysis. The script is downloadable here.
- Step 3 : Perform the Coverage Analysis
Finally, to generate a detailed coverage report, I used the following command:
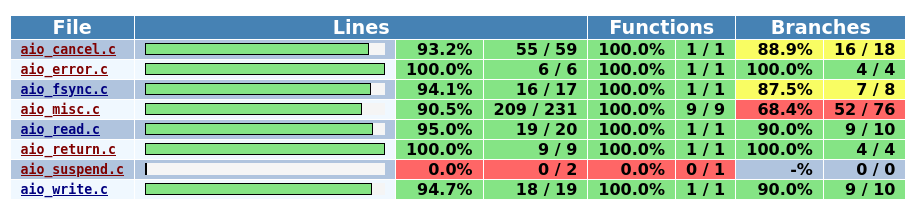
gcovr --gcov-executable sparc-rtems6-gcov --html-details ../coverage/aio-coverage.html --html-title "AIO Coverage" --gcov-ignore-parse-errors=negative_hits.warn --filter cpukit/posix/src/aio
This command runs gcovr to produce an HTML coverage report, here’s a description of the flags used:
--html-details ../coverage/aio-coverage.htmlgenerates a detailed HTML report and saves it as aio-coverage.html in the ../coverage/ directory.--html-title "AIO Coverage"gives the report a specific title, making it easier to identify.--gcov-ignore-parse-errors=negative_hits.warntells gcovr to ignore certain parsing errors that may occur.--filter cpukit/posix/src/aiorestricts the coverage analysis to the files related to the Asynchronous I/O (AIO) implementation.
This way I managed to generate a coverage report limited to the code i was interested in. Here’s a screenshot of the output i was able to see.